The Biggest Challenge with Digital Signing and How to Overcome It
- Rajesh Soundararajan
- Aug 02, 2022
- 2 min read
The Pros and Cons of Digital Signing
Digital signing has been prevalent for several years, providing a method to electronically sign, encrypt, and send documents to intended recipients. It is widely used for electronic deliveries and paper documents and has become a critical part of various industries, such as banking, education, healthcare, government, and trade.
The growing adoption of digital signing is due to the time and money saved compared to traditional mail or courier services. However, digital signing also has its challenges, including perceived complexity and limited accessibility. In this post, we will explore the advantages and disadvantages of digital signing and how secure QR code technology can address its challenges.
The Advantages of Digital Signing
Digital signing enhances document security by reducing the risk of interception and alteration of information.
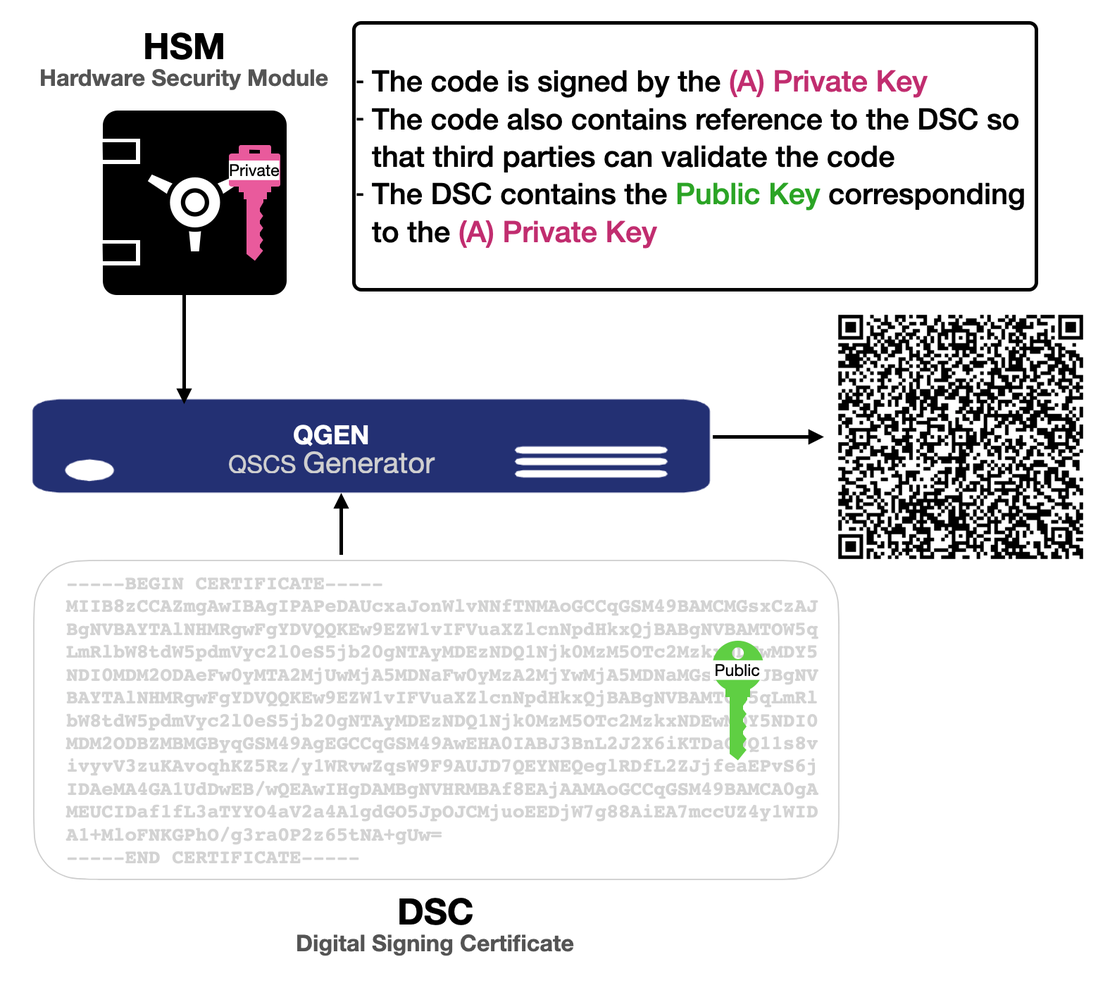
It serves as an electronic equivalent of a physical signature, allowing the signer to encrypt their signature with a private key.
Digital signatures rely on a mathematical/cryptographic scheme to ensure the authenticity of the data, making forgery detection easy.
The Biggest Challenge of Digital Signing
The main issue with digital signing is that it is perceived as too complex. Traditional methods often require specific readers or unique apps for verification, which are not suitable for mobile browsers or third-party validators. Additionally, recipients cannot validate digital signatures on printouts or scanned copies of documents, leading to frustration and confusion.
The Solution: Secure QR Code Technology
By integrating secure QR code technology with digital signing, we can achieve a simple, efficient, and effective solution that:
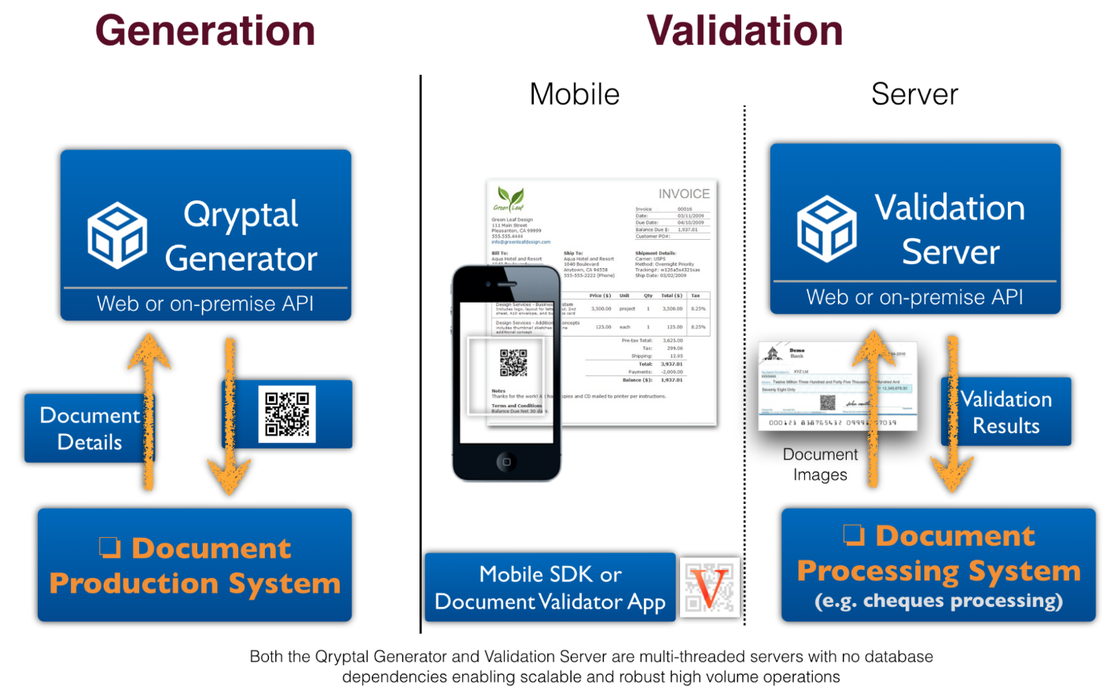
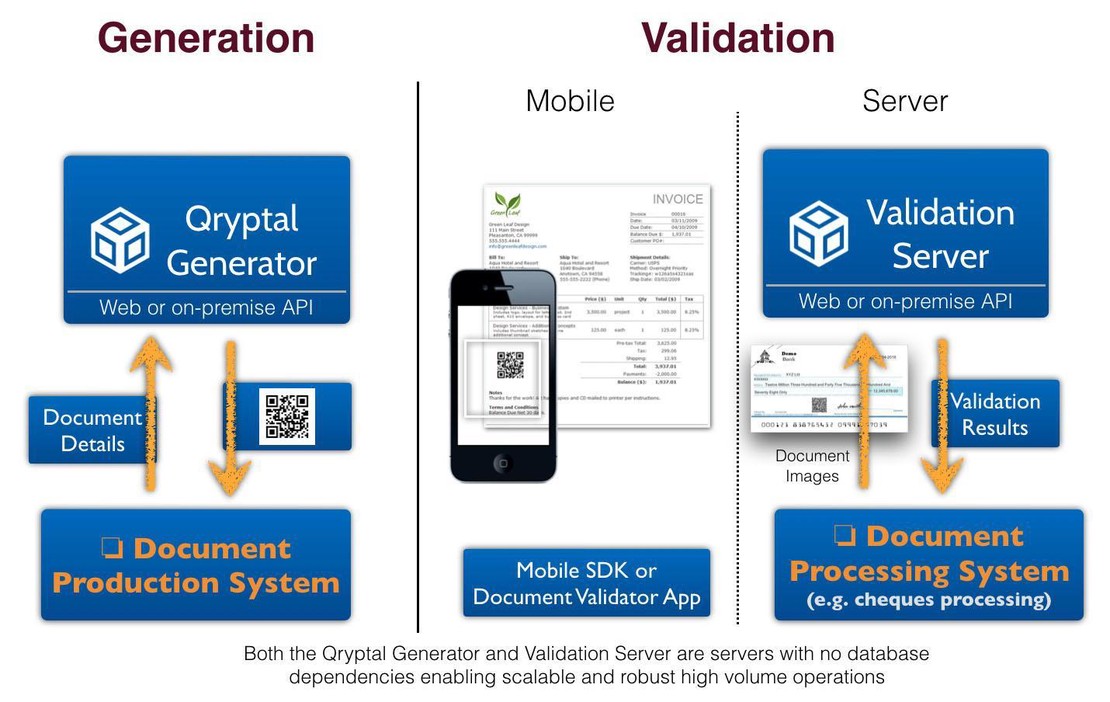
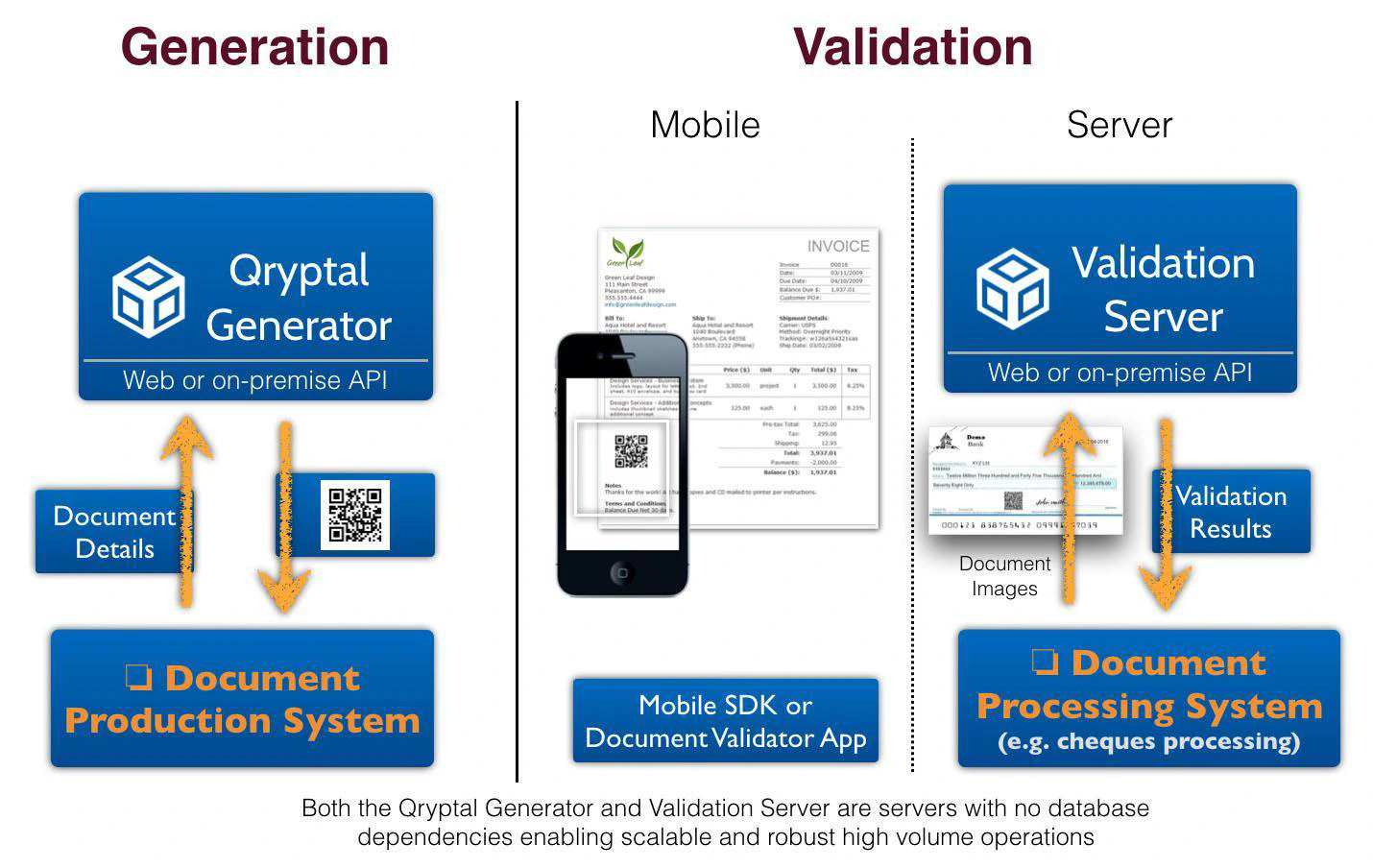
Plugs into existing document production systems and generates a secure digital signature with embedded data as a barcode for easy validation using a mobile browser or smartphone app.
Seamlessly integrates with existing systems, allowing for verification even on printouts or pictures of documents.
Utilizes a decentralized, server-less architecture for scalability and maintenance-free operation.
Employs PKI-based cryptography for enhanced security.
Enables offline verification through self-contained QR codes.
Works for both electronic and printed documents (phygital).
Protects customer and institutional privacy in a straightforward and logical manner.
The Generation and Validation Framework
The easiest way to evaluate this technology is by signing up for a free trial.
You may also like
- Digital Signing Certificate Management for generating EU Digital …
- QR Code Secured University Certificates and Transcripts for Higher …
- This is how countries should issue COVID-19 Vaccination Certificates
- Why does Secure QR code score over Blockchain?