QR Codes in 2022: Boon or Bane?
- Rajesh Soundararajan
- Mar 22, 2022
- 4 min read

The Rise of QR Codes: Convenience Meets Security
The past two years have witnessed an unprecedented surge in QR code usage across the globe, with masks and QR codes becoming ubiquitous during the pandemic.
In this two-part series, we delve into the current state of QR codes in 2022, examining their pros and cons. In this first installment, we discuss the rapid growth of QR code adoption worldwide. In the follow-up post titled- QR Codes in 2022: Creating Secure and Tamper-Proof QR Codes – we will outline the steps to ensure a secure user experience with QR codes and make them tamper-proof.
The two-dimensional QR code has become an essential tool, capable of conveying a vast array of information almost instantly through a simple mobile device scan.
Unlike barcodes, which store information only horizontally, QR codes hold data in both horizontal and vertical directions.
A QR code can hold 100X more information than a barcode, storing over 7000 digits or 4000+ characters.
QR codes can link to web pages (URLs), PDFs, text, and images.
Although QR codes have existed since their invention by Masahiro Hara, an engineer at Japan’s Denso Wave Corp., in 1994, their widespread use has only occurred in recent years. Hara initially envisioned QR codes for business purposes, never anticipating their widespread adoption for payments, electronic ticketing, and various other applications today.
Consumerization of QR Codes
QR codes are now an integral part of daily life, appearing on everything from local shops’ walls to COVID-19 test reports and vaccination certificates. Almost every product manufacturer or service provider uses them to fulfill specific objectives.

QR codes have become indispensable in industries such as payments and fintech, FMCG, retail, travel, hospitality, food, healthcare, and even donation platforms.
Customization of QR codes
Numerous websites and mobile apps offer free QR code creation and customization, allowing companies to build branding around their products or services.
QR codes can be easily scanned and verified using a smartphone or tablet.
Scanning of QR Codes
- QR codes can be scanned with a simple smartphone or a tablet.
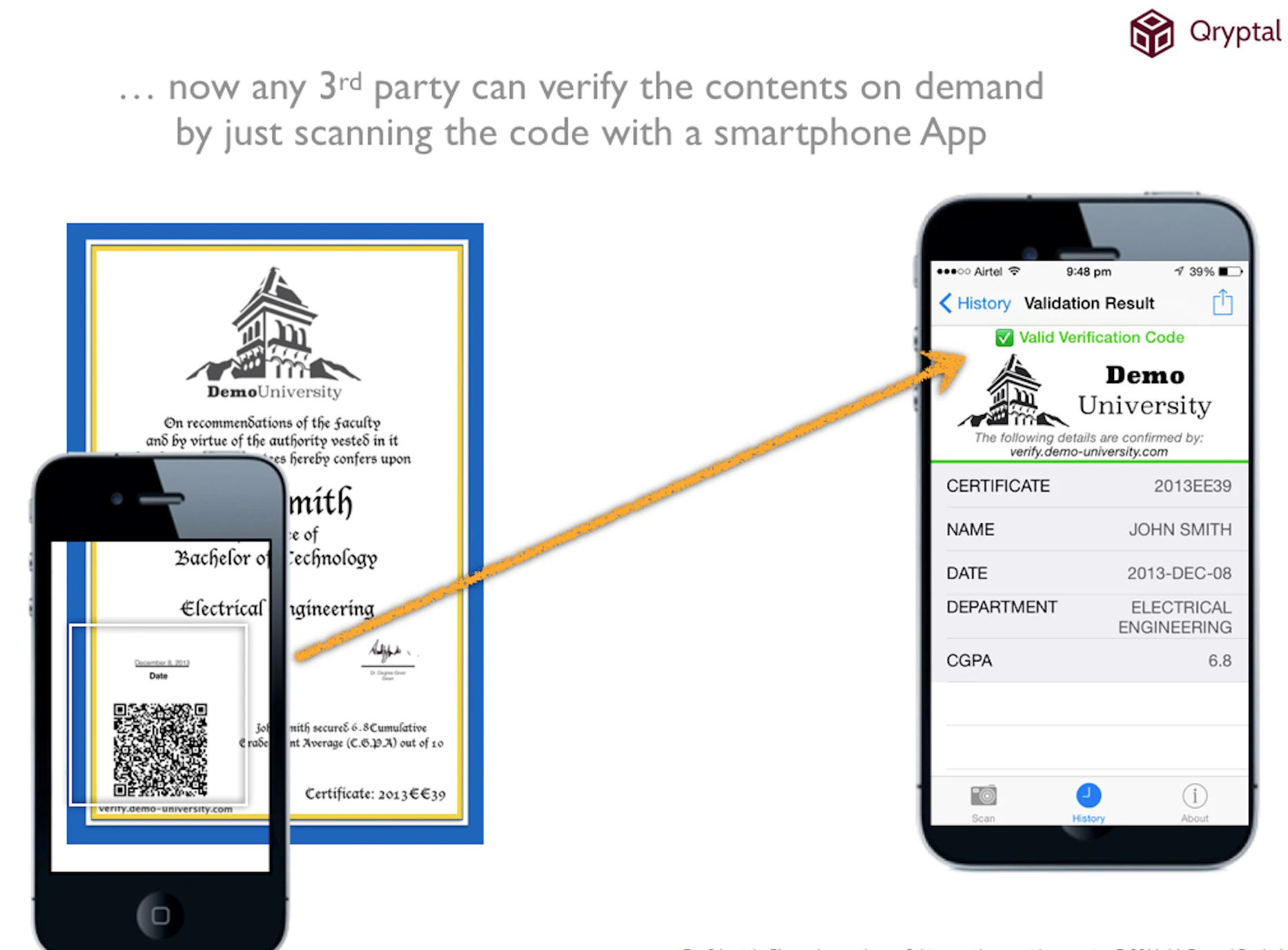
Figure 2 Image Source - /img/industries/scanning-the-code.png
Multiple Applications of QR Codes
QR codes connect the physical and digital worlds, offering versatile solutions for various industries.
Marketers use QR codes to disseminate product or service information.
Manufacturers help customers access product ingredients or contents with QR codes.
QR codes can provide information about manufacturing cycles and processing steps.
Sellers use QR codes to establish product authenticity.
QR codes enable traceability throughout the value chain.
QR codes can offer supporting information and documentation for better product understanding.
QR codes facilitate ESG (environmental, social, and governance) requirements.
QR codes enhance out-of-store channels, enabling easy and fast payment transactions.
QR codes complement traditional advertising by providing additional supporting information.
The hospitality and tourism sector, including Forex dealers, tour operators, airports, and large hotel chains, leverage QR codes for contactless services, such as scan-and-check-in options.
QR codes have revolutionized the travel industry, reducing crowding at counters and waiting areas.
The healthcare sector uses QR codes for services such as booking doctor appointments, patient registration, medication orders, and payments.
COVID Certificates and test reports
The use of QR codes on COVID-19 test reports and vaccination certificates for authentication purposes has been a game-changer. Scanning the code verifies the certificate’s authenticity, displaying either a “Certificate successfully verified” or “Certificate invalid” message.
Payments
QR code-based payments gained popularity globally after Asian payment companies and fintech players adopted them for instant transactions. Some non-profit organizations and charitable trusts saw scan-and-pay donations account for nearly 25% of total contributions during COVID-19.
Peer-to-peer and B2C payments have deepened in countries like India and China, where cash transactions were previously cumbersome. In India alone, over 10,000,000 merchants accept payments via QR codes.
A word of caution -
With such widespread usage, QR code issuers must ensure their codes are secure and tamper-proof. Scammers often exploit the rapid growth in QR adoption to deceive customers with fake codes. That’s why generating secure QR codes at the source is crucial.
In our next post - QR Codes in 2022: Creating Secure and Tamper-Proof QR Codes – we will discuss steps you can take in various use cases to ensure a secure QR code experience.
You may also like -
- Why does Secure QR code score over Blockchain?
- How does the Secure QR solution work?
- We were dissecting Coinbase’s US$14m ’lazy creative’ Super Bowl 2022 QR advert
- QR code’s role in the Ukraine-Russia conflict