Blockchain versus QR code– And the winner is….
- Rajesh Soundararajan
- Nov 09, 2021
- 8 min read
Secure QR ! It scores big on cost-effectiveness & low energy consumption
With the popularity of Blockchain continuing to grow and, in fact, gaining momentum through 2021, questions are being raised about its sustainability on two critical criteria. Energy consumption costs as well as transaction costs.
Close on the heels of #COP26, the question is if Blockchain’s popularity is expanding beyond banking - into other industries, such as healthcare, music, accounting, governments, and online marketplaces – is this sustainable?
Blockchain technology is still relatively new and unknown, yet many companies, industries, and governments are rushing into it. This is despite other proven technologies like QR code that helps in transactions & securing documents with seamless execution and transparency.
This post discusses the unstainable impact of energy and transaction costs in using Blockchain and how Secure QR can do a better job in some of the use-cases of Blockchain, especially relating to document security.
Differentiating Between The Transaction and Transaction Document
At this point, it is vital to note that most transactions have an output in the form of a document. This can be a physical document, as in most cases, or a digital document. In either case, the transaction output is captured as a document, where a secure QR comes in. In most cases, the transaction document (output) is tampered with and not the transaction itself.
One of the critical things for building sustainable and scalable technology is to adhere to global standards that withstand the test of time. Unfortunately, it usually takes years of pilot and actual use cases before the technology is proven. Secure QR code scores well on that front.
However, in the din of media hyperbole on the Blockchain, the progress made over the last decade on Secure QR codes is often missed. As a technology, QR code and Secure QR code technology has been adopted across the most prominent nations in the world like India and China over the last decade.
Blockchain Technology – Explained
Blockchain technology is a system for transactions that cannot be reversed or tampered with; it allows two parties to engage in secure digital transactions without a third party. It is a distributed digital ledger that records every transaction and broadcasts these transactions to an entire network of computers on a peer-to-peer system. The transaction is verified as authentic by all the participants in the network. This adds another level of security because each transaction is verified several times and is extremely hard to tamper with or falsify. Blockchain has been used in banking systems, food production systems, healthcare systems, and even vaccination drives in recent years.
The key elements of Blockchain are
immutability (cannot be changed or altered in an unauthorized manner),
distributed ledger (every participant can see all the transactions and verify and even keep a copy), decentralized (there is no single governing authority),
enhanced security (using hashing, encryption, and cryptography) and is based on consensus protocols.
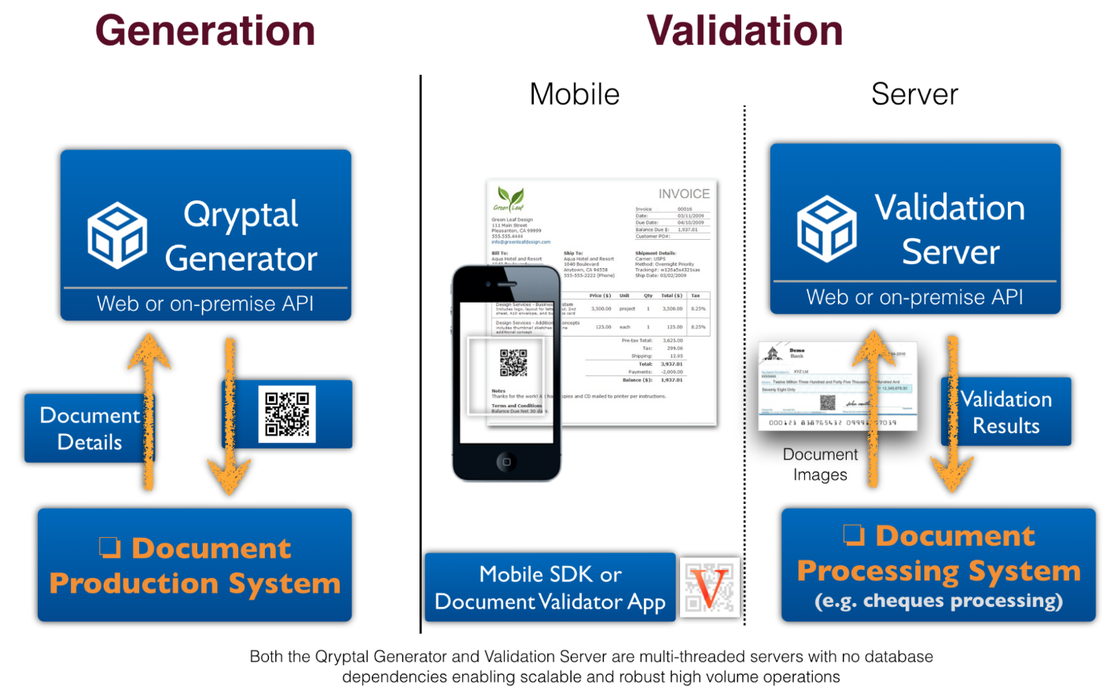
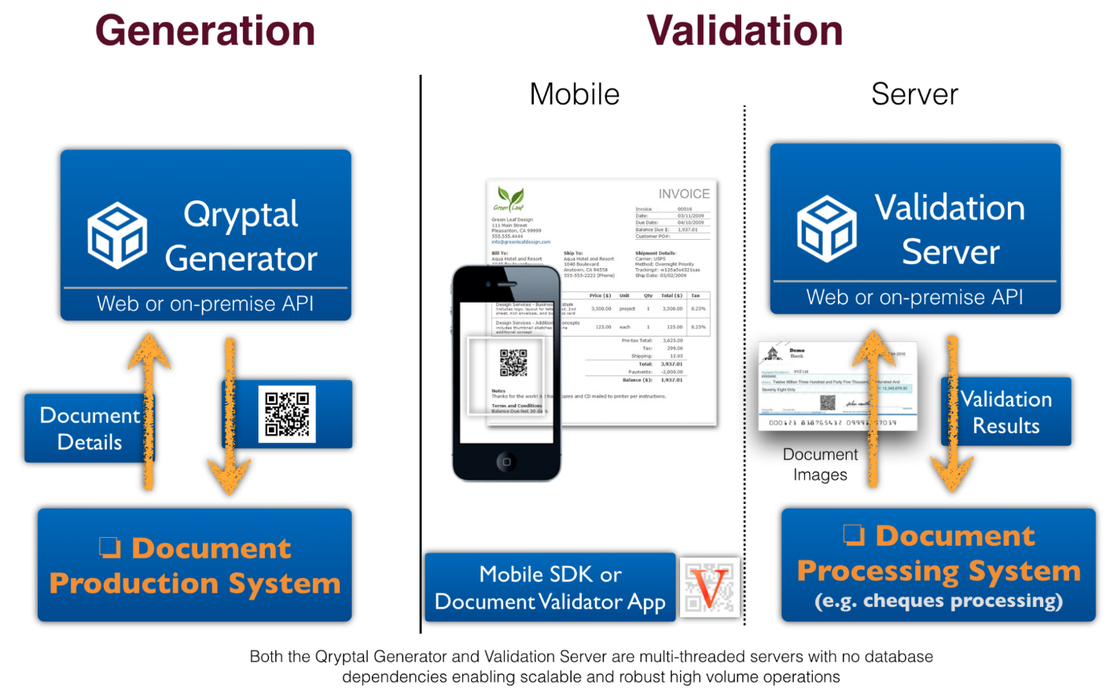
Qryptal’s Secure QR codes give us the same elements - information is secured at the time of generation using a unique private key under the issuer’s control only, thus preventing unauthorized alterations or tampering. The code itself can be thought of as - the ledger. It is based on standard cryptography and has high levels of security due to PKI. All that is needed for verification is the corresponding public key, which can be distributed as per the requirements and the transaction.
Secure QR Code Technology – Explained
As shared in our earlier post, the QR code is based on an open standard and scores because it has a high density of information per unit area. This, coupled with the explosive growth of smartphones giving everyone the capability to have a QR reader on demand, has helped QR code usage to grow exponentially over the last decade. However, the standard QR code faces a few challenges when security and secure documents transfers are involved.
QR Codes even today are commonly used for URL redirection to a web page or resource, but this can lead to QR phishing and is not suitable in case of security and making the information tamper-proof. . At Qryptal, we designed our Secure QR code solution to be secured with a private key of sufficient strength so that it cannot be tampered with.
Like in a blockchain, secured QR codes can be considered just like the immutable ledger (as it is tamper-proof and safe). And the benefit is that the validator-user can still validate without being part of a network (which is the requirement in Blockchain) as the verification is decentralized. Thus, secure QR codes combine the best of both worlds.
Qryptal’s secure QR uses similar digital signing commonly used in Blockchain at the generation of the code. There is no need to access any database or central ledger as the verification is decentralized. All that is required is the public key to verify the information is not tampered with. Hence, using blockchain-like asymmetric encryption and signing capabilities, secure QR codes help achieve the security of blockchain solutions at a fraction of the cost – on energy consumption and transactions.
Such a secure QR code solution allows for multiple use cases like cheques, ID cards, invoices, passports, school certificates, trade finance documents, vaccination certificates, to name a few. In addition, enterprises also benefit from simple integration using APIs into their existing ERP systems in an on-premises or cloud environment.
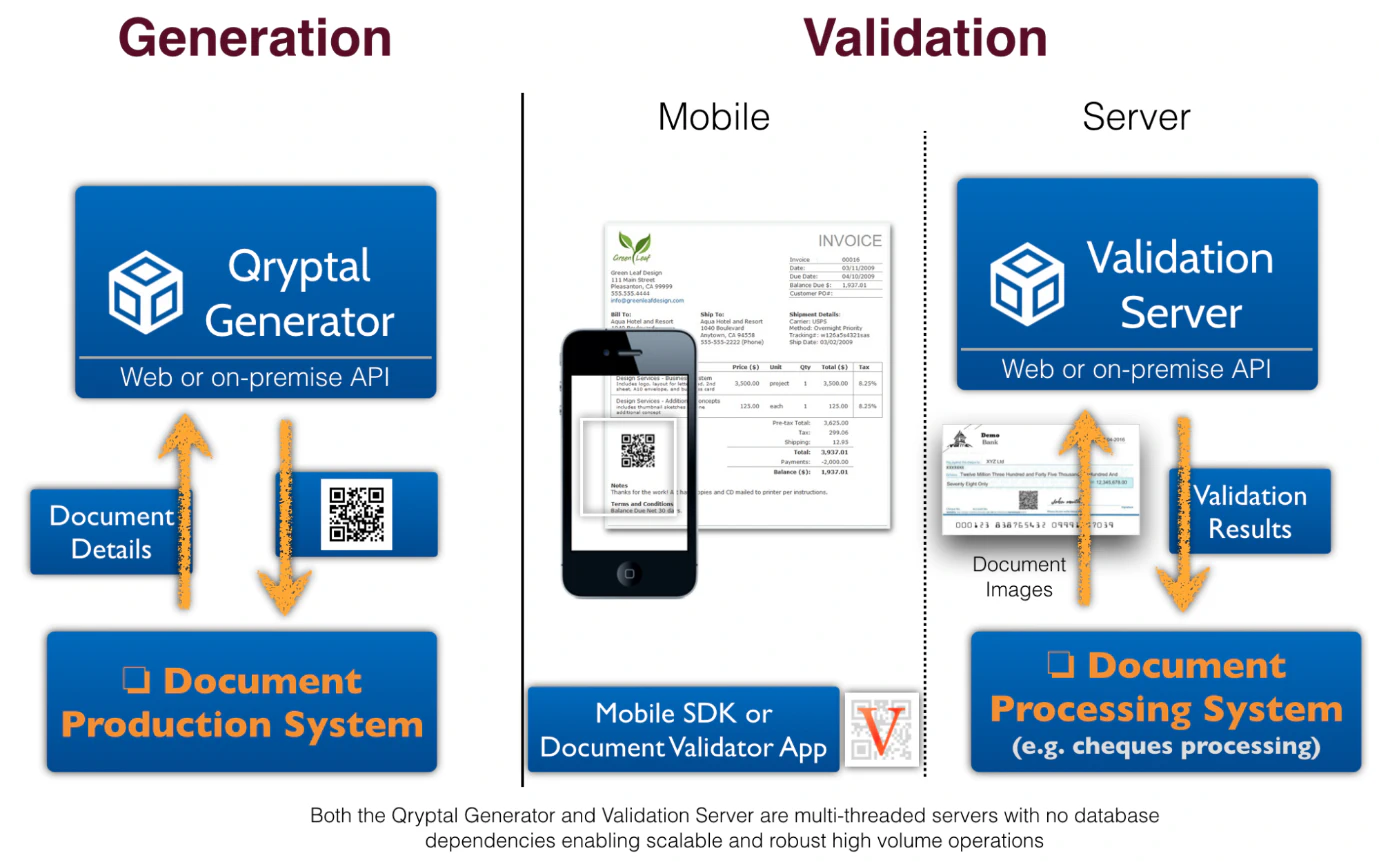
Secure QR Code Architecture
QR Codes - Proof Of Widespread Use At Low Cost
One of the best validations on the effectiveness and efficiency of QR code technology to drive transparency in healthcare transactions and authentications is India’s quick and efficient roll-out of QR code-driven COVID-19 vaccine certificates that were issued for over 1 billion transactions (doses) in less than a few months.
Another notable validation is the mass adoption of UPI as a payment facilitator across India with QR Code payments. It must be noted that UPI payments can leverage secure QR but is not dependent wholly on secure QR. In September 2021 alone, in just one month, India’s UPI records 3.65 bn transactions worth Rs 6.54 trillion (US$ 87.75 billion). China has always been ahead in using QR codes for payments - Alipay and WeChat being well known examples.
Both the above examples have used QR and not Blockchain for document validation or transaction processing. QR code technology has helped improve security and processing while dramatically reducing the costs to a few cents or even a fraction of a cent per document/transaction.
This alone has far-reaching implications for roll-out at scale. In addition, the proven technology has an architecture for secure generation of a transaction document and verification/authentication system for any 3rd party without complex infrastructure investment.
Finally, speed is the essence, and any roll-out can be done in days with proper planning.
Energy Consumption in Blockchain Is Unsustainable
According to the Cambridge Center for Alternative Finance (CCAF), Bitcoin consumes around 110 Terawatt Hours per year. That translates to about 0.55% of global electricity production—roughly equivalent to the energy use of a small country.
BBC News recently published that Bitcoin consumes ‘more electricity than Argentina’ - BBC News.
The average energy consumption for one single Bitcoin transaction in 2021 could equal several hundreds of thousands of VISA or MasterCard transactions. According to a source that tries to estimate the energy consumption of both Bitcoin (BTC) and Bitcoin Cash (BTH) over time. It does so by estimating how much income miners could spend on electricity, as no institution tracks how much energy the cryptocurrency consumes. This also applies to which countries mine the most Bitcoin, estimated by cross-referencing IP addresses.
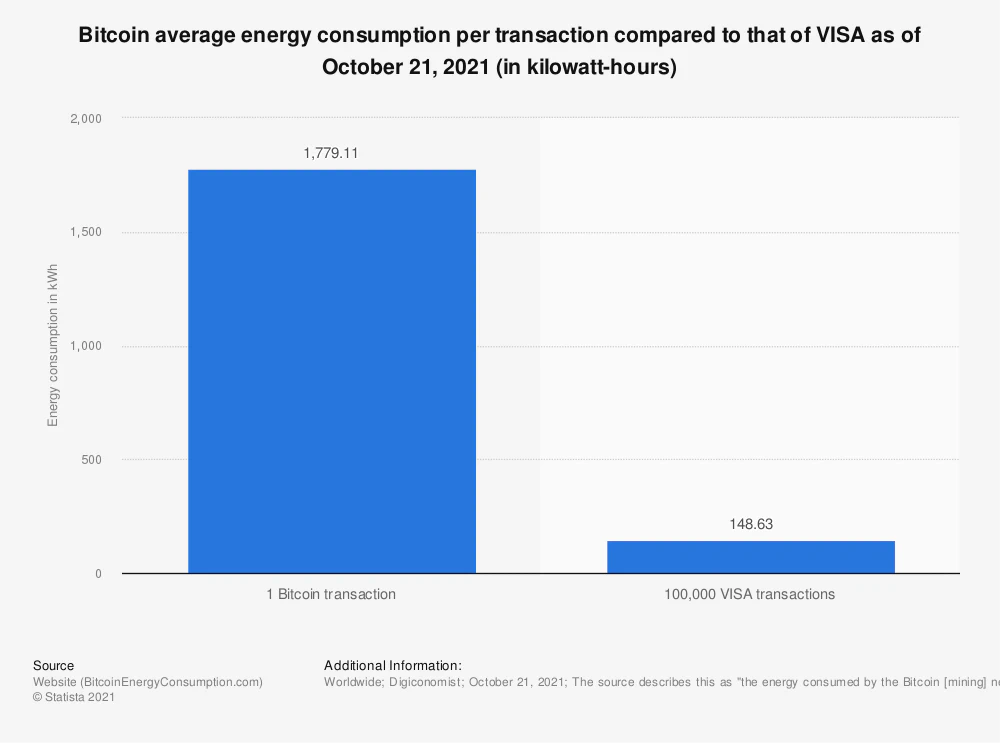
Bitcoin average energy consumption
Transaction Costs in Blockchain Seem Untenable
As shown on the the popular website blockchain.com, the cost per transaction has increased from $19 in 2011 to $215 in November 2021.
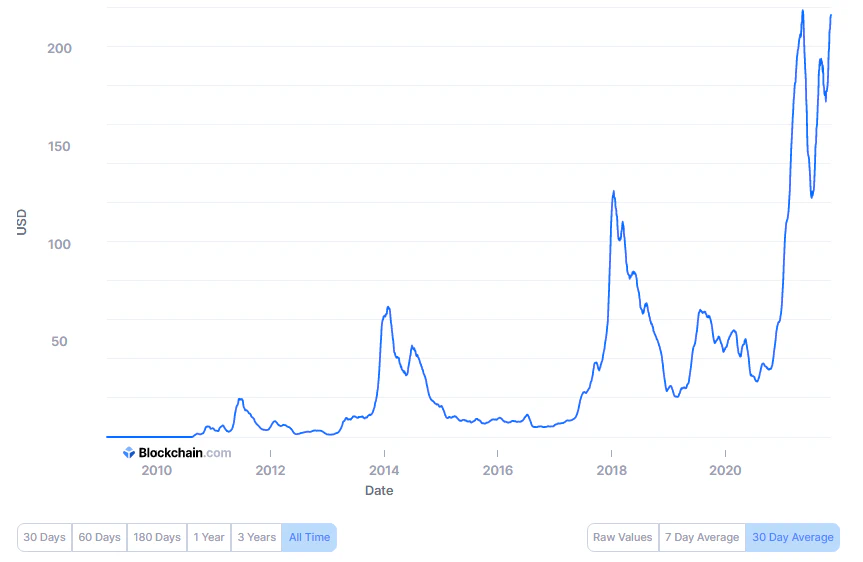
Blockchain transaction cost
In addition, there are substantial hidden energy consumption costs, complexity, management costs, and mining costs. Not just the upfront investment, but the ongoing expenditure and some of these costs are dramatically high. Much as it is spoken about as an effective solution for combating climate change, there is an argument that technologies like Blockchain consume far too much energy than what is stated.
Can Secure QR hold up to the Marketing Glitz of Blockchain?
The faster time to market, scalability, proven technology, efficiency, and effectiveness would make secure QR code technology far more attractive for banks, financial institutions, healthcare industry, and even the retail sector in developing countries compared to Blockchain.
In China and recently in India, the modest and unassuming QR code has helped the governments, large enterprises, millions of small businesses and billions of users achieve a lot more at a fraction of the cost in two of their most significant initiatives in recent past – vaccinations as well as payments.
With the ability to democratize access, efficiency, wide acceptance, and effectiveness – it would be naïve for large governments and businesses to jump onto Blockchain at the expense of secure QR codes, without due diligence. Especially on the parameters of sustainability. Secure QR codes as technology can transform physical-digital transactions at a fraction of the cost of blockchain systems, delivering speed and efficiency both in implementation and integration. With the power of mobile phones in the hands of consumers and the need for secure technologies, the world is at a cusp of transformation, and a secure QR code holds the key to large scale adoption.
You may also like -
- Why does Secure QR code score over Blockchain?
- Why Having Immunity Passports on Blockchain is a bad idea
- Australia’s Fake Vax Certificates, Blockchain, and QR Codes